October 10, 2015
Some specifics: Our proposal for a Health & Work Service
In our August 2015 proposal to the SSDI Solutions Initiative sponsored by the Committee for a Responsible Federal Budget on Capitol Hill, we recommended that a community-focused Health & Work Service (HWS) be established. The services to be provided by the HWS are generally not available in our country today, particularly to lower-wage workers and those who work for small firms.This service would be dedicated to responding rapidly to new episodes of health-related work absence among working people in order to help them:
— Minimize life disruption and get things back to normal as quickly as it is medically safe to do so
— Focus attention on treatments and services to restore ability to function at home and at work
— Understand and navigate through the healthcare and benefits programs and systems
— Avoid being abandoned; learn how to be a squeaky wheel and get their needs met
— Communicate with all parties to expedite both medical care and the return to work process, including resolving non-medical obstacles to recovery and return to work, making temporary adjustments or arranging reasonable accommodation when appropriate.
— Keep their jobs or promptly find new ones if that is necessary.
(The material below summarizes our written proposal. If you’re interested in the scientific research that underlies these ideas, the 30+ pages and 3 appendices of our “real deal” formal report support all key assertions with literature citations and an extensive bibliography. Along with the 12 other proposals commissioned by the SSDI Solutions Initiative group, it is scheduled to be published electronically in late October, and in print in January 2016.)
The first few days and weeks after onset are an especially critical period during which the likelihood of a good long-term outcome is being influenced, either favorably or unfavorably, by some simple things that either do or do not happen during that interval. It is the optimal window of opportunity to improve outcomes by simultaneously attending to the worker’s basic needs and concerns as well as coordinating the medical, functional restoration, and occupational aspects of the situation in a coordinated fashion.
The best opportunity for basic intervention appears to last about 12 weeks or three months, although some data shows it ending by 6 months. Many studies have show that a modest set of simple services—that embody an immediate, systematic, pro-active, integrated, and multidimensional approach—can mitigate the potentially destructive impact of common injuries, illnesses, and chronic conditions on quality of life among the working population.
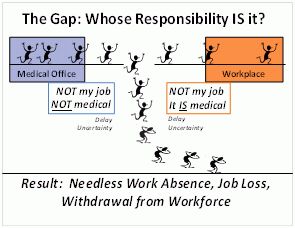
In the USA today, a large and growing fraction of Social Security Disability Insurance (SSDI) awards are being made to people deemed totally unable to work due to conditions that are among the most common health problems in America and the world, but which only rarely cause permanent withdrawal from the workforce. Low back pain and other chronic musculoskeletal conditions (MSK), and common mood disorders (CMD) —particularly depression and anxiety—are the most prominent conditions in this category.
Near-immediate assistance from a community-focused Health & Work Service will allow people with these kinds of common conditions to avoid the kind of adverse secondary consequences they too often experience today. Those consequences are usually not obvious until months or years later, after unfortunate things have happened. The unlucky ones have received sub-optimal health care, been left with under-treated or iatrogenic impairment, become dependent on opioids, found themselves socially isolated, lost their jobs, withdrawn from the workforce, lost economic independence, and ended up on long-term disability benefits programs or SSDI in order to survive. Anticipatory programs that ensure the right things happen from the start and include early identification of those needing extra support are the simplest and most effective way to prevent later adverse secondary consequences of these conditions.
As we envision it, the HWS will build strong collaborative relationships with referral sources in local communities: treating physicians, employers, and benefits payers. Service delivery in individual cases can be largely telephonic and internet-based because these technologies are proving to be as or more effective than face-to-face care delivery. The quadruple goal is to maximize service quality, optimize outcomes, minimize logistical challenges, and control costs. The HWS service will:
(a) — get its referrals from affected individuals, local treating physicians, employers, benefits payers and others when work absence has lasted or is expected to last more than four weeks;
(b) — champion the stay-at-work and return-to-work (SAW/RTW) process from the time of referral through the end of the immediate response period (usually 12 weeks post onset);
(c) — quickly evaluate the individual’s situation, screen for known risks for poor outcomes, help them make a SAW/RTW plan and support them in carrying it out;
(d) — facilitate communications among all involved parties as needed to get everyone on the same page and driving towards the best possible outcome.;
(e) — expedite and coordinate external medical, rehabilitative and other kinds of helping services, including referrals for specialized services as needed to address remediable obstacles in a variety of life domains;
(f) — take a problem-solving approach in collaboration with affected individuals, their treating physicians, employers, and payers.
Of course, developing the HWS will first require a commitment to funding, either by the government or by a foundation that is committed to system change. Once that has been obtained, the initiative will unfold in a series of steps including design, prototyping, development, and field-testing in different geographies, followed by a large randomized controlled trial. After that, the HWS can gradually roll out across large geographic areas.
What does this mean for you? First, if you like the idea of working people getting the kind of support they need and deserve — and when it is most likely to make a difference, please support this idea in whatever way you can. Why not call or email your Congressman? Second, if you are a professional with the expertise and passion required to help people get “right back on the horse” — and are now stymied and frustrated by the current system’s inadequacies / dysfunctions, you have probably realized that the HWS service might create a lot of fulfilling and satisfying jobs for specialists like you. If so…. that’s another reason to call or email your Congressman!